What is R_0?
A key quantity in epidemiology is ![]() : the basic reproduction number (which you may have heard about in the news).
: the basic reproduction number (which you may have heard about in the news). ![]() , is the number of people that a given person is likely to infect. A good diagram of this is shown below for Ebola with
, is the number of people that a given person is likely to infect. A good diagram of this is shown below for Ebola with ![]() and the 2002 SARS outbreak with
and the 2002 SARS outbreak with ![]() . Given that the number of people to whom an infected person is likely to spread the disease will depend on mitigation measures,
. Given that the number of people to whom an infected person is likely to spread the disease will depend on mitigation measures, ![]() will change over the course of the outbreak. A disease with
will change over the course of the outbreak. A disease with ![]() will continue to spread (the number of people continues to grow), meanwhile
will continue to spread (the number of people continues to grow), meanwhile ![]() results in the number of cases declining. Given that
results in the number of cases declining. Given that ![]() is just a number of people, it is a unit-less number.
is just a number of people, it is a unit-less number.
Our goal
Measure ![]() for different stages of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States during 2020.
for different stages of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States during 2020.
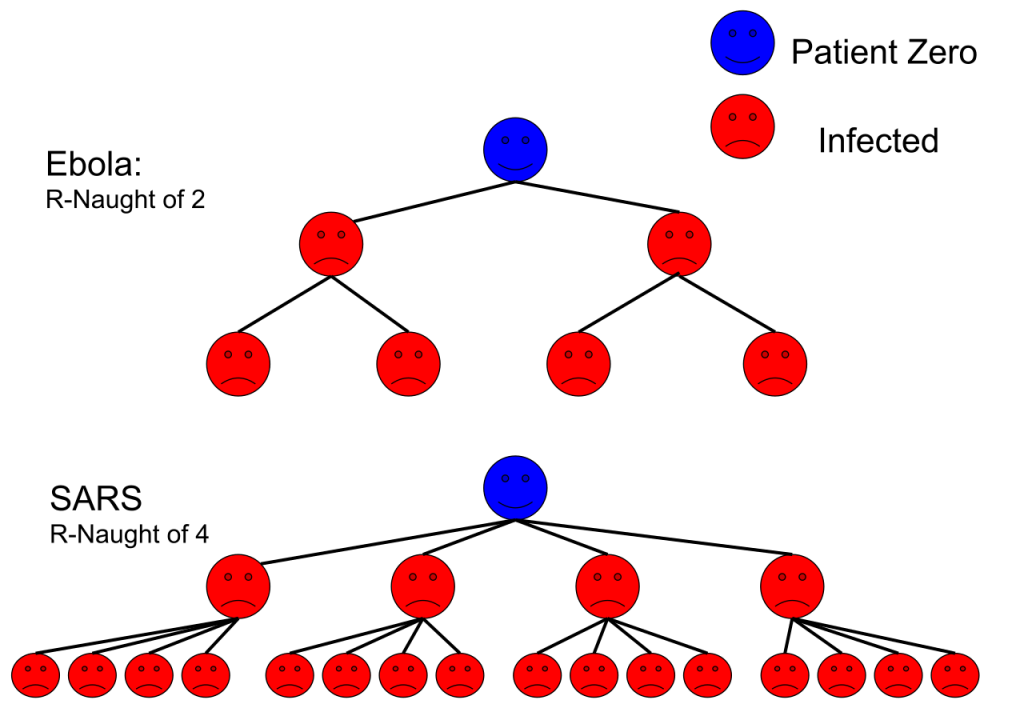
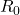 is the average number of people infected from one other person, for example, ebola has an
is the average number of people infected from one other person, for example, ebola has an 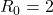 , so on average for every one person who has ebola they will pass it on the two other people.
, so on average for every one person who has ebola they will pass it on the two other people.KieraCampbell, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons.

