Unit II On-a-Page
Terminology

Instructor’s Note
This Unit is very heavy on vocabulary, so there is a set of flashcards on Quizlet to help you.
- An is a lens or mirror.
- An is the apparent reproduction of an object, formed by an optical element (or collection of them) reflecting and/or refracting light.
- Images can either be (same orientation as object) or (upside-down with respect to object).
- The optical axis is a line that passes through the optical element perpendicular to it
- The point where the optical axis meets the optical element is called the .
- The of a lens is where the lens is thickest (for a converging lens) or thinnest (for a diverging lens).
- The of a mirror is the center of curvature.
- Image
 and object
and object  distances are measured along the optical axis.
distances are measured along the optical axis. - Signs are relative to the path of the light.
- If the object is on the same side as the incoming light, then
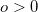 , otherwise
, otherwise 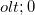 .
. - If the image is on the same side as the outgoing light, then
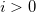 , otherwise
, otherwise 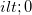 .
. - For a lens, the incoming and outgoing sides are different (light goes through a lens).
- For a mirror, the incoming and outgoing sides are the same (light bounces off a mirror).
- Focal lengths are also signed. If the element tends to incoming parallel light (a or a ), then the focal length is negative. If the element incoming parallel light ( or ), the focal length is positive.
Principles for Unit II
This unit in particular has a lot of terminology. To help you stay focused, the principles (where we will begin analyzing situations) are:
How light interacts with surfaces and materials
- Law of reflection, which is best understood in the particle picture.
- Law of refraction, which is best understood in the wave picture.
- Light slows when it enters a medium, but the energy of a photon cannot change. So the wavelength must!
Optical elements and ray diagrams
- The position of the image formed by an optical system is located at
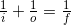 where:
where:
 is the object distance, using the sign conventions used above.
is the object distance, using the sign conventions used above. is the image distance, using the sign conventions used above.
is the image distance, using the sign conventions used above.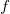 is the focal length with its correct sign.
is the focal length with its correct sign.
- For ray diagrams: one ray in parallel and out through the focal point, one ray in through the focal point and out parallel, one ray using the center of the system.
- And point where photons seem to emerge can be used as an object. Such a point could be a real source of photons (an object) or an image from another optical element.
A lens or a mirror
The apparent reproduction of an object, formed by an optical element (or collection of them) reflecting and/or refracting light.
When the image is the same orientation as the object
When the image is upside-down with respect to the object.
The point where the optical axis meets the optical element.
For a lens, where the lens is thickest.
For a mirror, the center is the center of curvature.
Spread the light rays apart.
a concave lens in which light rays that enter it parallel to its axis bend away (diverge) from its axis
A mirror that bends away from the light source
Bring light rays to a point.
a convex lens in which light rays that enter it parallel to its axis converge at a single point on the opposite side
A mirror that bends towards the incoming light

