Discussion 2: Electric Flux
Instructions: Upload your work as a pdf document. All responses must be typed. Any calculations must be done using Latex, an equation editor, or typed. You can insert diagrams and pictures where appropriate but pictures of your hand written responses and calculations will not be accepted.
The Area Vector
The area vector, ![]() , is used to describe a flat surface.
, is used to describe a flat surface.
- Place a piece of graph paper on a tabletop. When describing the graph paper using the area vector, what would the magnitude represent?
- When describing the graph paper using the area vector, what would the direction represent?
- If you were to draw an arrow to represent the area vector, in what direction would it point?
- When describing each square on the graph paper using the area vector
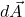 , what would the magnitude and direction represent?
, what would the magnitude and direction represent? - Fold the graph paper so that you form a triangular tube. How many area vectors are now required to describe the graph paper?
- Roll the graph paper into a cylindrical tube. When the paper is formed this way, does the area vector
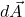 still accurately describe each square?
still accurately describe each square? - Why or why not?
Electric Flux and Gauss’ Law
Figure 1 shows the demonstration we did in Lesson 7 where we modeled a uniform electric field with evenly spaced lasers.

- Compare the magnitude of the electric field at points A and B.
- Explain the reason for your answer to question 9.
In Figure 2, a Gaussian cylinder is in the presence of a uniform electric field. The electric field is lined up with the cylinder’s axis.
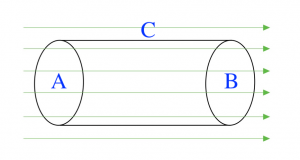
- What is the electric flux through surface A?
- What is the electric flux through surface B?
- What is the electric flux through surface C?
- Is the electric flux positive, negative, or zero through surfaces A, B, and C?
- Is the net electric flux through the entire Gaussian cylinder positive, negative, or zero?
- Explain your reasoning for question 14.
In Figure 3, a point charge of +Q is insider a Gaussian cylinder.
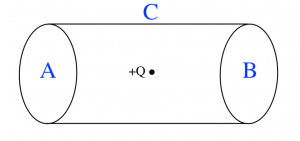
- Is the electric flux positive, negative, or zero through surface A?
- Is the electric flux positive, negative, or zero through surface B?
- Is the electric flux positive, negative, or zero through surface C?
- Is the net electric flux through the entire Gaussian cylinder positive, negative, or zero?
- Explain your reasoning for question 19.
